
Documentation site for django-carrot
View the Project on GitHub chris104957/django-carrot
Getting started
Install django-carrot
Install with pip
pip install django-carrot
Install RabbitMQ
Install and start RabbitMQ:
brew install rabbitmq
brew services start rabbitmq
Configuring your Django project
- Add carrot to your Django project’s settings module:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
#...
'carrot',
]
- Apply django-carrot’s migrations them to your project’s database:
python manage.py migrate carrot
For see all configuration options, refer to :ref:carrot-settings
Starting the service
Once you have configured django-carrot, you can start the service using the following django-admin command:
python manage.py carrot_daemon start
The daemon can be stopped/restarted as follows:
python manage.py carrot_daemon stop
python manage.py carrot_daemon restart
For the full set of options, refer to admin-command
Creating and publishing tasks
While the service is running, tasks will be consumed from your RabbitMQ queue. To test this, start the django shell:
python manage.py shell
And use the provided helper, carrot.utilities.publish_message:
from carrot.utilities import publish_message
def my_task(**kwargs):
return 'hello world'
publish_message(my_task, hello=True)
The above will publish the :code:my_task function to the default carrot queue. Once consumed, it will be
called with the keyword argument hello=True
Task logging
In order to view the task output in :ref:monitor, you will need to use Carrot’s logger object. This is done
as follows:
from carrot.utilities import publish_message
import logging
logger = logging.getLogger('carrot')
def my_task(**kwargs):
logger.debug('hello world')
logger.info('hello world')
logger.warning('hello world')
logger.error('hello world')
logger.critical('hello world')
publish_message(my_task, hello=True)
This will be rendered as follows in the carrot monitor output for this task:
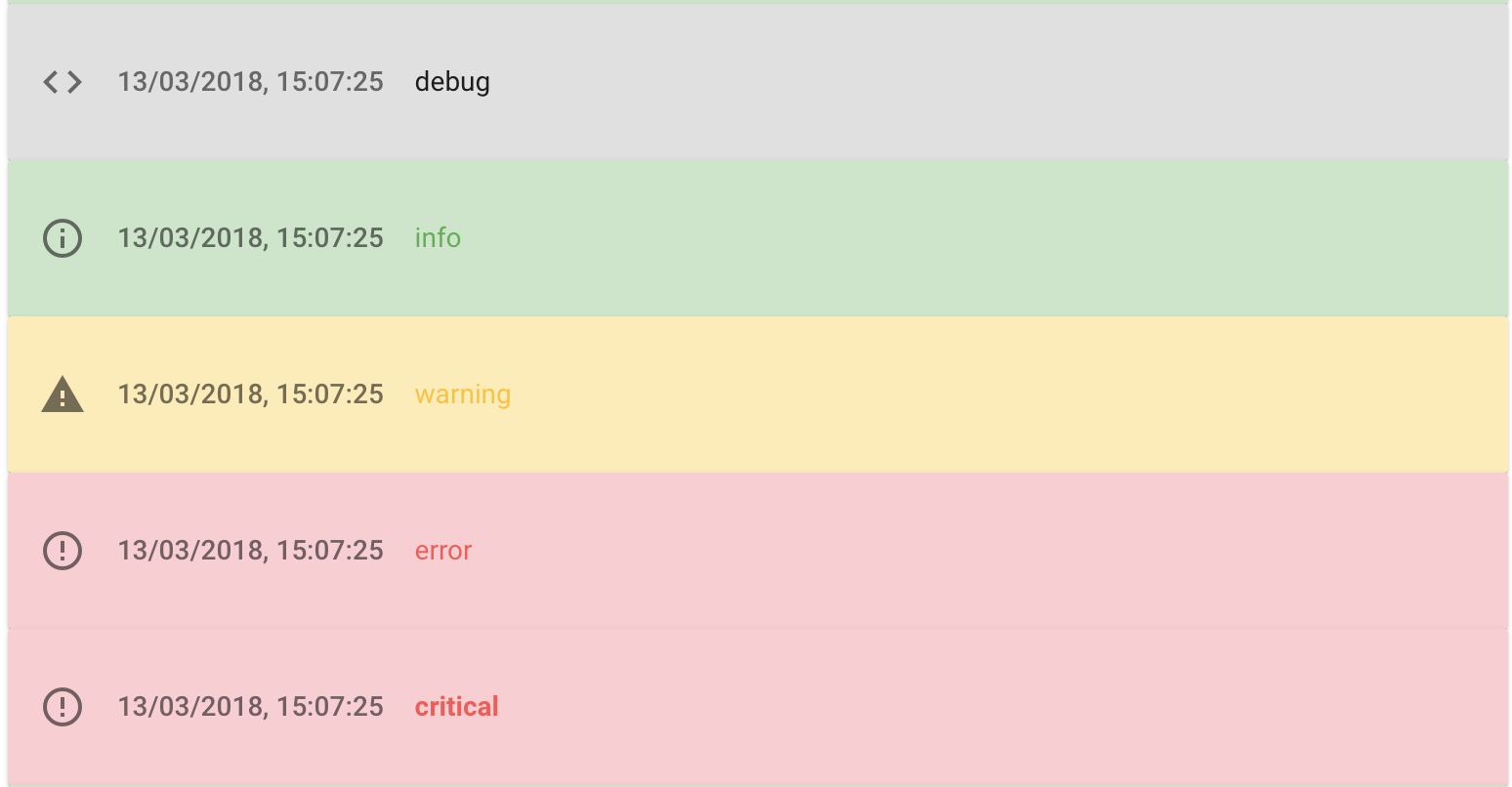
By default, Carrot Monitor only shows log entries with a level of info or higher. The entry logged with
logger.debugonly becomes visible if you change the Log level drop down
Scheduling tasks
Scheduled tasks are stored in your Django project’s database as ScheduledTask objects. The Carrot service will publish tasks to your RabbitMQ queue at the required intervals. To scheduled the my_task function to run every 5 seconds, use the following code:
from carrot.utilities import create_scheduled_task
create_scheduled_task(my_task, {'seconds': 5}, hello=True)
The above will publish the my_task function to the queue every 5 seconds
Tasks can also be scheduled via the :ref:monitor
The Carrot monitor
Carrot comes with it’s own monitor view which allows you to: - View the list of queued tasks - View the traceback of failed tasks, and push them back into the message queue - View the traceback and output of successfully completed tasks
To implement it, simply add the carrot url config to your Django project’s main url file:
urlpatterns = [
#...
url(r'^carrot/', include('carrot.urls')),
]
For more information, refer to the carrot monitor
Docker
A sample docker config is available here
Support
If you are having issues, please Log an issue
License
The project is licensed under the Apache license.